What is a smart factory?
How the smart factory can drive value?
How organizations can begin enacting a comprehensive smart factory?
Would manufacturing small and medium enterprises (SMEs) be able to afford the cost of purchasing and maintaining smart factory solutions?
These are the common questions most manufacturers have. The smart factory is a concept that has different visions, for some, it is just a higher level of automation, while for others it is an integration of shop floor decisions with the enterprise. However, a truly smart factory exhibits a fully connected flexible system that has the capability to self-optimize the performance & autonomously run across a wide network of the production process.
So, what makes a smart factory different from traditional automation?
The smart factory is a connected, optimized, data-driven, predictive and agile system. It leverages both physical and digital technologies to gather, exchange and use information that can be transparently utilized across networked interactions between man, materials, machine, and systems.
Automation in manufacturing has existed for decades now, then why shift to the smart factory concept?
Business Process Automation (BPA) as a way to enable flexibility, efficiency, and responsiveness within the organizations.
The top four factors that necessitate this shift are:
- ‘Do more with less’- It helps to leverage the emerging technologies that can reduce the modern production complexities that have limited resources.
- ‘The desire for customization’- Smart factory allows you to be agile, proactive, and connected to address the desire for customization.
- ‘FOMO’ (Fear of Missing Out)- Smart Factory can help navigate competitive pressure and stay ahead of the curve.
- ‘Human Factor’- The dearth of trained workers also prompts many manufacturers to go smart.
How the smart factory can drive value?
- Reduced waste production
- Shorter time-to-market
- Effortless monitoring
- High production speed
- Improved quality of standardization
- Reduced dependency on human labor
- User-friendly controls
- Real-time intelligence
- Optimized asset utilization
- Safety & sustainability
With the impetus to answer the posed question on how organizations can begin developing a comprehensive smart factory? Here’s a four-layer smart factory concept
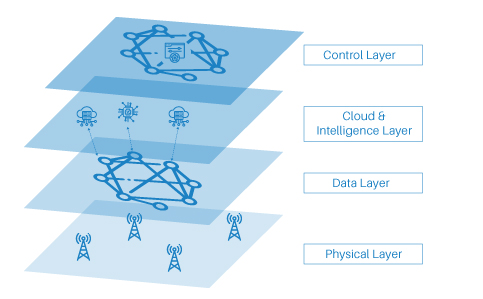
At the physical layer, all machines, the shop floor as a whole, and those activities actually taking place physically are assigned, while the data layer incorporates the process wherein the data is transferred from the machines (i.e sensors embedded in machines) to the cloud and vice versa, and a system is controlling what data is sent/received and at which rate. The data is further stored & processed, in the cloud by sophisticated analytics. At the top layer, control & supervision takes place. One can adapt the master program controlling system with human intervention whenever necessary.
Most of the smart factory visions that exist today lack the concept for SMEs & do not characterize affordability in terms of financial investment & technical constraints. The problems, needs, and capabilities of SMEs are different and they face many difficulties to realize such smart factories that hinder their adoption. SMEs require a robust adoption strategy that is consistent with their circumstances.
For the manufacturing decisions to be accurate and consistent, data need to be integrated into manufacturing and IT technologies. The first step therefore for SMEs is, to discover the data present and its correspondent dimension under SME. The next step would be to perform a readiness assessment that can help determine the readiness of an SME in terms of finance and technology & correspond it with the employee’s skills available. The third step would be to design a smart factory vision considering digitization, advanced manufacturing & data analytics capabilities, followed by identifying the tools & practices like design & simulation toolbox, sensors & connectivity toolbox, robotics & automation, etc that are essential to accomplish the vision.
SMEs can start with maximizing the performance of a single asset and then gradually moving towards the performance optimization of a series of assets, plant, and a factory network.
Final Thought:
The Smart factory paradigm enables a competitive edge for large enterprises and SMEs with its infinite possibilities. Investing in a smart factory concept can enable manufacturers to stand out from the rest and function more effectively and efficiently in an ever-more complex and dynamic ecosystem. It entails more than a set of connected assets and empowers manufacturers to address complex issues and unlock value by making manufacturing smarter. SMEs can choose the technologies carefully to fulfill their goals, as some manufacturers compete via speed, quality, and cost, the smart factory technologies that help to market faster, increase quality, and reduce per-unit costs can be selected. Others may choose to focus on the product customization and fulfillment models and invest in other technologies.
Wondering which technologies your organization should choose? Connect with our experts, they are seasoned to guide you on your journey towards becoming a ‘Smarter Factory’.





